Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors Mnemonic
Jail cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors
A peptidoglycan monomer consists of ii joined amino-sugars, Northward-acetyl glucosamine (NAG) and N-acetyle muramic acrid (NAM), with a pentapeptide coming off of the NAM. So, a peptidoglycan monomer is a NAG-NAM-pentapeptide. These peptidoglycan monomers are synthesized in cytosol and transported across cytoplasmic membrane past Bactoprenols (BP). Transglycosylase (Transglycosidase) enzymes insert and link new peptidoglycan monomers into the breaks in peptidoglycan (chain elongation). Finally, transpeptidase enzymes reform the peptide cross-links between the rows and layers of peptidoglycan to make the wall potent (cantankerous-linking).
Enolpyruvate transferase converts UDP-N-acetylglucosamine to UDP-N-acetylmuramic acid. L-alanine racemase, forms D-alanine from Fifty-alanine, and D-alanylalanine synthetase (ligase) incorporates D-alanine into the pentapeptide.
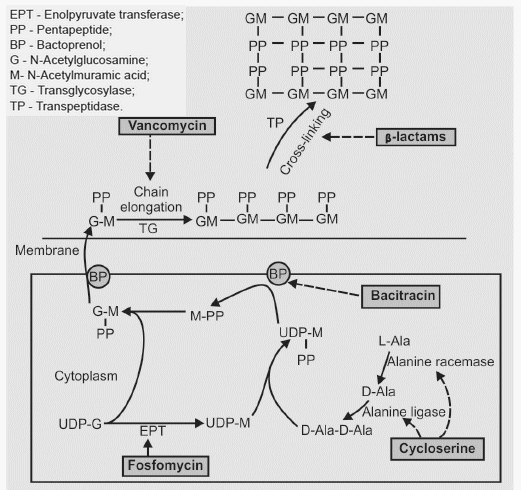
Mnemonic: Firmly Demark to Bacterial Prison cell Vall – EaT BAT
The cell wall inhibitor antimicrobials and the steps they inhibit are:
- Fosfomycin: Enoylpyruvate transferase (EPT) – NAG to NAM conversion
- Beta-lactam: Transpeptidase (TP) – Cross-linking
- Bacitracin: Bactoprenol (BP) dephosphorylation (Transfer of NAG-NAM-pentapeptide from cytosol to cell membrane)
- Cycloserine: Alanine racemase and ligase (Pentapeptide formation)
- Vancomycin: Transglycolase (Chain elongation)
All these drugs are BACTERICIDAL.
Beta-lactams include: Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Monobactams and Carabapenems
Mycobacterial cell wall = Peptidoglycan + Mycolic acid + Arabinogalactan
- Isoniazid and Pyrazinamide: Prevents mycolic acid synthesis (Activeness of pyrazinamide is often mentioned equally unknown in books)
- Ethambutol: Prevents mycolic acrid incorportation into cell wall (inhibits arabinogalactan transferase)
All 1st line ATT drugs are bactericidal except ethambutol which is bacteriostatic.
Fungal cell wall = Beta-glucan polymers equivalent to bacterial peptidoglycan
- Echinocandins: Inhibit beta-glucan synthesis (fungicidal confronting yeasts like candida and fungistatic against molds)
Translation Inhibitors
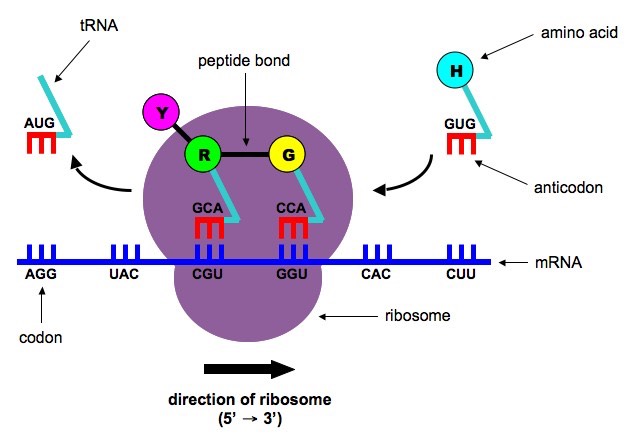
We tin understand the translation using a cook book analogy. Suppose:
- Restaurant = Prison cell
- Recipe book = Dna
- A single recipe page = Gene
- Photocopier = RNA polymerase
- Photocopied recipe page = mRNA
- Chef and his spectacles = Ribosome (Suppose 50S ribosome is the chef and 30S ribosome is his spectacles)
- Kitchen easily = tRNA
- Ingredients = Amino acids
- Final food = Protein
Chef reads photocopied recipe page and kitchen hands bring ingredients to the chef to make nutrient (protein).
a. Tetracycline and Tigecycline: Prevents coming together of kitchen hand with the chef (demark to 30S subunit of ribosome and interfere with binding of tRNA to ribosomal complex)
b. Aminoglycosides: Replaces the spectacles of chef, and then that he reads the recipe incorrectly (demark to 30S subunit of ribosome and causes mRNA codon to misread)
c. Linezolide (Oxazolidinone): Doesn't permit chef to wear spectacles to start cooking (bind to 50S subunit of ribosome and prevents formation of 50S/30S initiation complex)
d. Macrolides, Clindamycin (Lincosamides), Streptogramins (Quinupristin, Dalfopristin) and Pleuromutilin: Prevents chef from reading of further steps in photocopied recipe folio (demark to 50S subunit of ribosome and prevents translocation-motion of ribosome along mRNA)
e. Chloramphenicol: Prevents kitchen banana from adding ingredients (bind to 50S subunit of ribosome and prevents peptide bond germination)
f. Rifampicin: It amercement the photocopier (inhibits RNA polymerase)
Mnemonic: ATT 30 and CELLS 50
- Binds to 30S: Aminoglycoside, Tetracycline, Tigecycline
- Binds to 50S: Chloramphenicol, Erythromycin (Macrolides), Linezolid, Lincosamide (Clindamycin), Streptogramins (-pristins)
Mnemonic: Take the 1st letter of the alphabet of drug for mechanism of action
- Tetracycline and Tigecycline: inhibits incoming T-RNA zipper to ribosome
- Aminoglycoside: Alters ribosome
- Linezolid: Link disruption between 50S and 30S ribosome
- Chloramphenicol: Chain elongation inhibition of poly peptide
- Rifampicin: RNA polymerase inhibitor (inhibits transcription)
- All other: Preven translocation
All these drugs are BACTERIOSTATIC except Aminoglycosides and Streptogramins.
Affecting Jail cell Membranes
a. Polypeptides: Polymixin B, Colistin, Tyrothricin (Binds to lipopolysacharide and phospholipid of outer cell membrane in gram negative organism and eventually breaks inner jail cell membrane besides; bactericidal)
b. Glycolipopetides: Daptomycin (disrupts the activeness potential of gram positive cell membrane; bactericidal)
c. Polyene: Amphotericin B, Nystatin, Hamycin, Natamycin (Binds to ergosterol; fungistatic)
d. Azoles: Ketoconazole, Fluconazole, Itraconazole (Inhibits ergosterol synthesis by inhibiting fourteen-alpha-demethylase; fungistatic against yeasts and fungicidal against molds)
e. Allylamines: Terbinafine, Naftifine (Inhibits ergosterol synthesis by inhibiting squalene epoxidase; fungicidal)
Affecting DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis inhibitor:
- Dna gyrase inhibitor: Fluoroquinolones (bactericidal)
- Dihydrofolate synthase inhibitor: Sulfonamides, PAS, Dapsone
- Dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor: Trimethoprim, Pyrimethamine, Proguanil
These Sulfone drugs are BACTERIOSTATIC.
DNA destruction: Metronidazole (free nitro-radicals; bactericidal confronting anaerobes) and Nitrofurantoin (bacteriostatic)
Antibiotic combinations
- Bacteriostatic + Bacteriostatic = Condiment
- Bactericidal + Bactericidal = Frequently condiment and sometimes synergistic
- Bactericidal + Bacteriostatic = Additive if lower sensitivity to bactericidal drug and Antagonistic if college snesitivity to bactericidal drug

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler means to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music.
Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors Mnemonic,
Source: https://epomedicine.com/medical-students/antimicrobials-simplified-mechanism-actions/
Posted by: galindowhistamed1951.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors Mnemonic"
Post a Comment